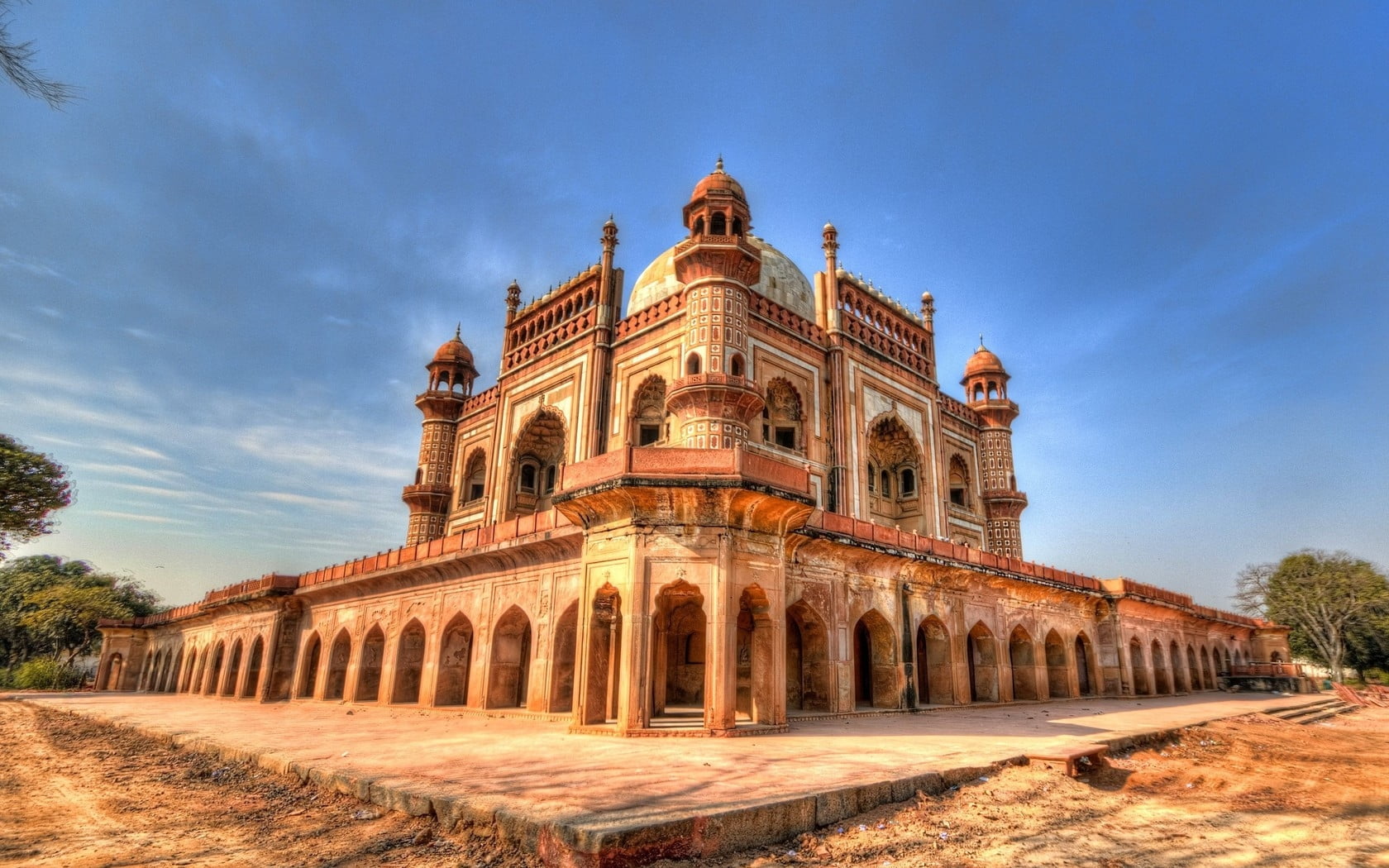
Whether it is the splendidness of the Taj Mahal or the intricacies of the Red Fort, the Mughal architecture of India provides evidence of a heavy cultural heritage and architectural prowess. In this article, we show that the Mughal architecture had a unique and rich history and culture, highlighting the key features, which include the geometrical intricacies, ornamentation, and many more of the famous monuments, and also the evolution, influence as well as the conservation of this architecture.
Introduction
The architecture of the Mughals is a special style of architecture that came to be regarded as a dominant style in the Indian subcontinent during the Mughal Empire which ruled for about three hundred years. This art form does not only symbolize a combination of Persian, Islamic, Indian, and Turkish architectural elements – but also magnificent and magnificent buildings unmatched by any.
History of Mughal Architecture
The influence of Mughal architecture is a part of Emperor Babur who is considered the builder of the Mughal dynasty. While in above he achieved great heights. The next three emperors of the Mughals Akbar, Shah Jahan, and Aurangzeb, gained their glory in Mughal architecture. The emperors who were much enriched by the different cultures had the opportunity to attain immortality through their architectural constructs.
Influences from Different Cultures
The Mughal architecture was a combination of Hindu and Muslim cultures influenced by Persians, for example, their skilful tile work and geometric patterns, and Indians, famous for their earlier use of beautiful and striking carvings and vibrant colours. These entities got connected to create artworks that were one of their kind and had interesting and beautiful design features.
Mughal Dynasties and The Atmosphere They Brought to Architecture
Akbar, the Sultan who was known for his forward-looking outlook, launched numerous architectural projects, among them is the building of Fatehpur Sikri, a city known to be large and impressive. In comparison, Shah Jahan has been regarded for his patronisation of the arts, which is prominent in his construction of the Taj Mahal, an undying symbol of love and comeliness.
Mughal Architecture Main Subsidiaries
It has several distinctive qualities that distinguish Mughal architecture from the design of other periods. The use of Red sandstone and marble; these two materials have been used throughout the ages and are associated with power and splendour Along with the decorative element the Mughals looked at the material which was used in the construction. The main materials used which gave Mughal architecture its distinct character are red sandstone and marble. These structural components not only give stately regard to the monuments but also promote their strength and resistance to the destruction of time.
Domed Roofs and Minarets
Dome tops and minarets modelling are among the most distinguishing features of Mughal architecture which combine their decorative and structural functions. The domes stand as soul-filled celestial yearnings, but minarets provide the unparalleled vision for the call to prayer as well as the presence of a dominant architectural element showcasing the mosque.
Symmetry and Balance
Symmetry and proportionality are principal rules of Mughal architecture, implying satisfaction with the system and orderliness. All that we see in the Mughal structures must be in an organized form in which every element is minutely measured for aesthetic value.
Incorporation of Gardens
Many Mughal architects used gardens in their creations to add both a productive but also an aesthetically appealing element to the abundance of urban settings. These detailed gardens contrast with rhythmic and luxurious vegetation and flowers, which produce a serene atmosphere without disturbing other building themes.
Mughal Style Architecture
With a whole lot of palaces that are masterpieces of Mughal architecture, Mughal art bestowed upon mankind several world-famous monuments which interest the visitors as much for their beauty and grandeur now as much as they were back then.
Taj Mahal
The Taj Mahal, probably the most loved and symbolic of all Mughal monuments, being a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is a memory of eternal love. The mausoleum was built by the order of Shah Jahan for his heartthrob wife Mumtaz Mahal It became known for its intricately carved and symmetrically adorned marble facade, and beautifully designed gardens.
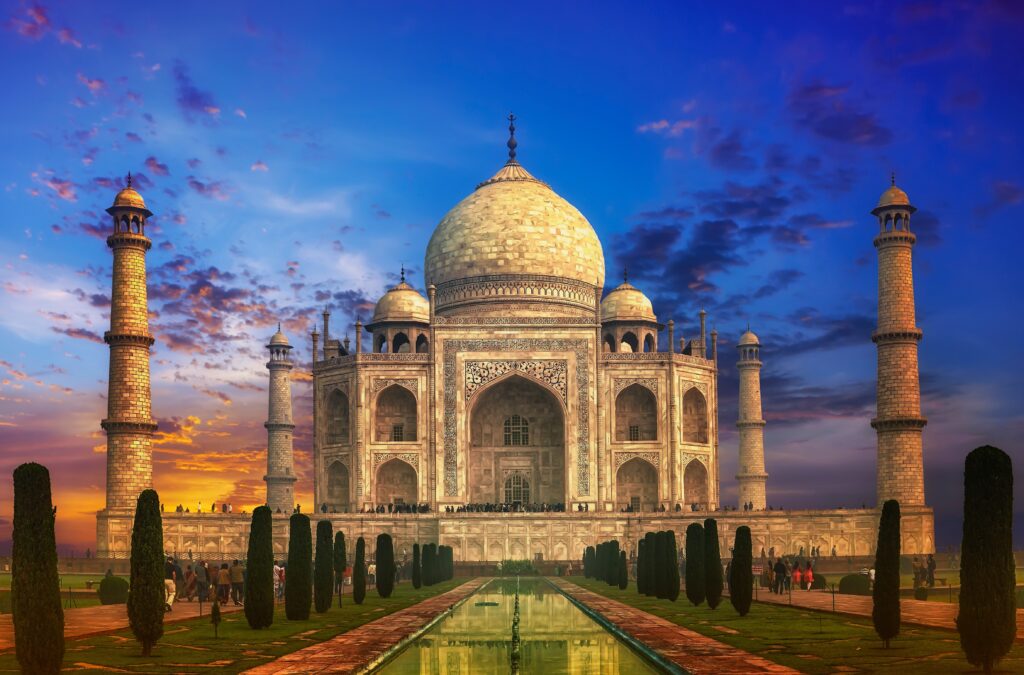

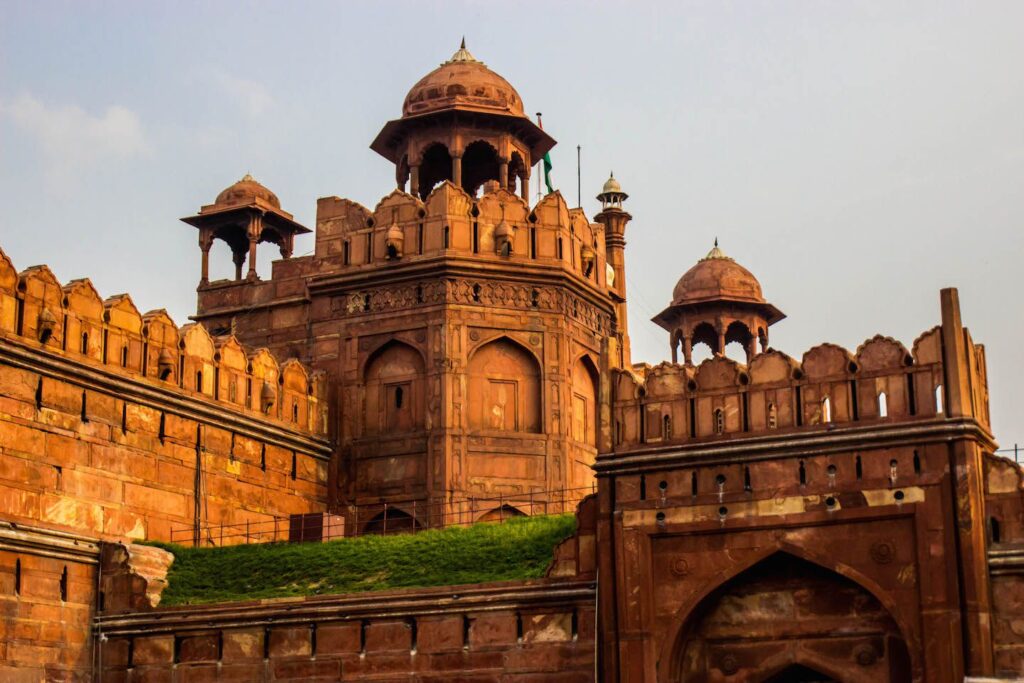
Red Fort
Situated in Delhi, Red Fort is an architectural scene just like it was even to the Mughal emperors for nearly 200 years. Undoubtedly, they were constructed majorly from red sandstone, an architectural element which is very well showcased in its imposing walls, ornate gateways and palaces, therefore, creating a visual example of the opulent lives the Mughal ruled lived.

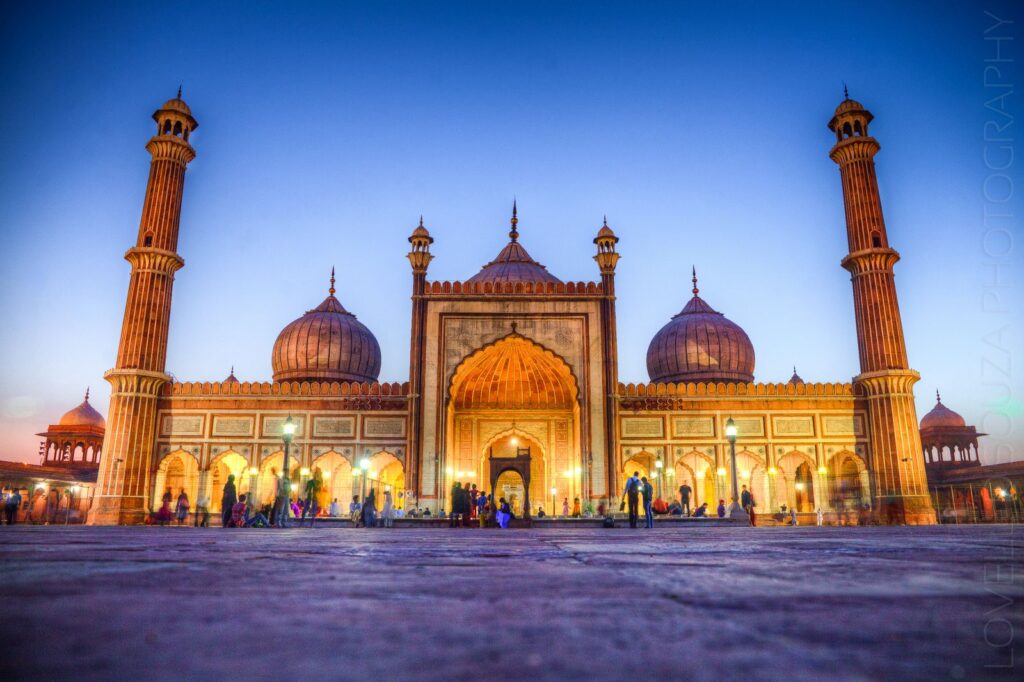
Jama Masjid
The Jama Masjid which was constructed by Emperor King Shah Jahan is one of India’s largest mosques and a marvel of the Mughal architecture. It boasts its sky-shooting minarets and delicate marble domes as well as a spacious courtyard and it is just one of the focal religio-cultural sites.

Evolution of Mughal Architecture
Along its course, the Mughal architecture experienced progressive development, and most impressively it preserved all the cultural features in harmony with the period, next to the technical innovations that made it more detailed and sophisticated, and lastly variations from political events that modified the look of the Mughal art.
Development Over Time
Mughal architecture can be described as a progression from the early constructions of concave designs to the Most exquisitely arabesque embroidering patterns as seen in the Mausoleum of the Taj Mahal. Creativity was unleashed, and old systems were revised as well as upgraded to adapt to new requirements as well as trends.
Impact of Political Changes
The political uprising and dynastic regime change used to put Mughal architecture in a much more dramatic way. The loss of the Mughal Empire in the 18th century was the factor that saw limited patronage and thereby led to the dismissal of some projects and discontinued the others.
Influence of Mughal Architecture
The Mughal architecture which emerged in India continues to stretch its boundaries beyond Indian borders by leaving a distinct footprint in the architectural domain of our world.
Legacy in Modern Architecture
The stylistic elements of symmetry, balance, and gravity are the most notable facets of Mughal architecture which have impacted leading modern architects and designers even now. Although the Mughal era was not tangible in the architecture between 1947 to 2000, the noticeable features of Mughal-era buildings can be visualised in the existing structures prevailing in government buildings or residential complexes.
UNESCO World Heritage Sites
The number of monuments belonging to the Mughal period, which have been acknowledged as UNESCO World Heritage Sites, emphasizes the universal presence and the cultural worth of such places in the world. Among others, these “sites” catch up to millions of visitors each year and thus serve the preservation and celebration of Mughal heritage.
Preservation of the Mughal monuments remains a challenge. It is not that Mughal buildings are not beautiful enough to survive, but they need to be preserved by all means possible.
Environmental Factors
Pollution, weathering and natural disasters often will affect the maintenance of Mughal structures very much. Mughal architectural constructions are not exempt from this constant threat. Activity should be carried out to lower the level of these risks. That can be done through a rigorous process of maintenance and R & R.
Tourism Impact
The number of visitors could also exhaust the monuments of the Mughal Empire, propelling their overcrowding, destruction and vandalism.
wear and tear. Practices and measures of visitor management are indispensable for the conservation of these sites since they guarantee their security in the long run.
Conservation Efforts
However, fortunate are the efforts engaged in the preservation and protection of Mughal monuments for the futurecveneorsof mankind. These days governmental agencies, conservation institutions as well and localisation communities are working in a coordinated manner to implement cultural conservation projects, carry out research activities and create awareness about the people’s heritage.
Conclusion
The Mughal architecture in the end could be said to be a clear proof of the intelligence, inspiration, and talent of builders of the Mughal dynasty. Starting from the precious domes of the Taj Mahal to the holy walls of the Red Fort, these centuries-old monuments still evoke an indescribable feeling of awe and admiration, either from tourists or historians, hence today Indians yearn for India’s glorious past and cultural heritage.
—
FAQs About Mughal Architecture:
- It is worth asking what were the most typical materials used in Mughal architecture.
- When red sandstone and marble were a preferred material, the construction of the Mughal architecture is famous for its long-lasting and superior decorative qualities.
- To what extent did the Mughal garden symbolize the Mogul architecture?
- Mughals’ parks became an essential part of a building’s scheme including the calming natural spaces which supplemented the splendour of the encompassing buildings.
- Is it only the Taj Mahal or any other Mughal structure which is of any great importance?
- The Taj Mahal represents the summit of the Mughal era architecture and illustrates its ungraded artistic spirit, expressive power of handiwork, and symbolic meaning of love.
- What transformation in politics did bring in the Mughal architecture?
- Political uprootings and dynastic shifts virtually shaped Mughal architecture which to a great extent directed the mechanical processes of patronage and novel architectural styles.
- Have Mughal monuments been encountered in respect of conservation or have their conservation led to more challenges?
- Mughal monuments are facing multiple problems among which we can consider environmental factors, tourist influence and protective attempts aimed at the sustainable protection of the monuments.