The Battle of Delhi in 1803 was a turning point in Indian history, showing the confrontation of the British East India Company and the Maratha Confederacy for dominance in the Indian subcontinent. This article tackles the complexities of this significant war by looking into its causes, methods, events, consequences, and heritage.
Introduction
The Battle of Delhi was not just a small-scale fight but a result of geopolitical problems and imperial dreams. The British East India Company entered India and soon faced the weakening Maratha Confederacy, which began the great confrontation.
Background of the Battle
During the late 18th and early 19th centuries, the British East India Company became the dominant force in trade and power, driven by the Company’s profitable trade and expanding its territory. On the other hand, the Maratha Empire, once a strong power, was faced with internal debate and the absence of unified leadership.
Importance of the Battle
The wildcard of the Battle of Delhi would define the future of northern India, which means that the Battle’s outcome would determine the British rule in India. Therefore, the political situation of the subcontinent would change for years to come.
Causes of the Battle
Expansionist Policies of the British East India Company
Fueled by commercial needs and the aspiration for territorial control, the British East India Company initiated an aggressive policy of annexation, which was all about subduing the Indian princely states and asserting British power.
Maratha Confederacy’s Weakness
Internal splits, succession problems, and the deterioration of the central power weakened the Maratha Confederacy, thus making it very vulnerable to external attacks and, at the same time, providing a chance for the British East India Company to take this chance and to use these fissures of the Maratha Confederacy.
Preparation and Strategies
British East India Company’s Military Buildup
The British East India Company realized that the city of Delhi was significant and sent troops, artillery, and other military equipment for a campaign.
Maratha Confederacy’s Defensive Measures
Knowing the danger the British were in, the Marathas fortified the essential locations, gathered their troops, and sought to make alliances with other Indian rulers to fight the British’s hegemony.
Deployment of Forces
British Forces: Strength and Composition
General Gerard Lake commanded the British East India Company to put a well-organized and disciplined force consisting of infantry, cavalry, and artillery into the field, further supplemented by the troops of the Company’s loyal natives.
Maratha Forces: Strength and Composition
The Marathas formed the Maratha Confederacy under the leadership of Daulat Rao Scindia and his general, Jaswant Rao Holkar, and they brought together many soldiers from different Maratha clans and allied states to fight as a solid but different coalition.
Key Events Leading to the Battle
British East India Company’s Ultimatum
In the way of power, General Lake threatened the Maratha leadership and asked them to obey the British rules; otherwise, he would use the military to get their terms.
Maratha Response
The Marathas did not give in to the British demands and decided to keep Delhi and fight the British army that came from the British to Delhi; hence, the climax of this stand-off between the Marathas and the British was the showdown that followed.
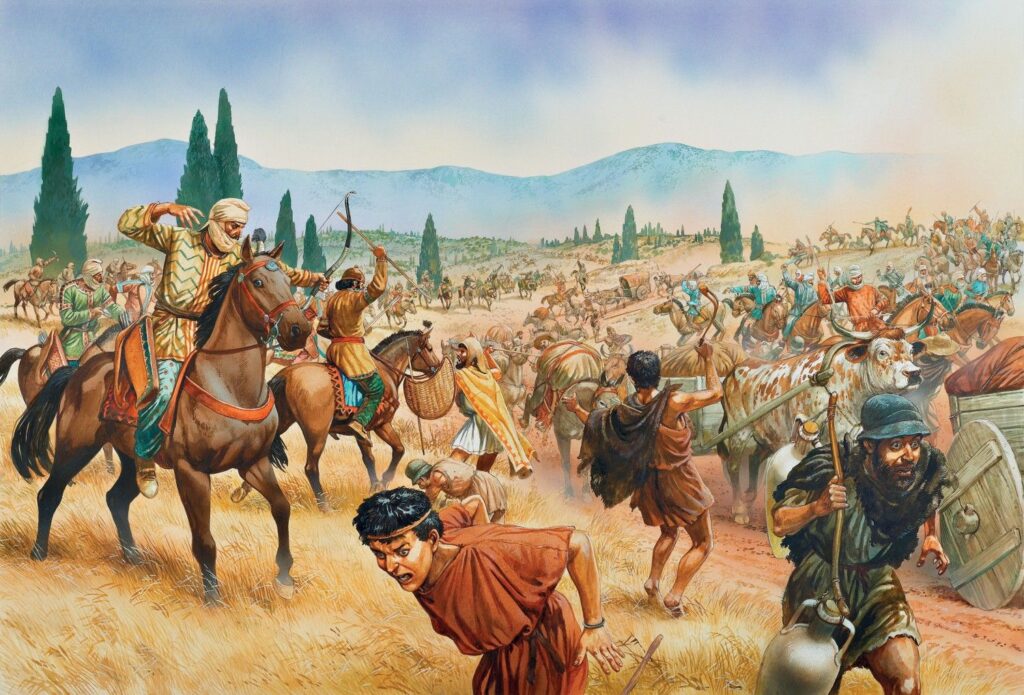
The Battle Begins
Initial Skirmishes
The outskirts of Delhi were the scene of the battles and surveillance as the British and Maratha scouts fought against each other, testing their defenses and probing for weaknesses.
Major Engagements
The crucial moment they had arrived when the two armies met in a series of pitched battles, each trying to win the right to control the strategic positions and the critical landmarks in the city.
Turning Points
Tactical Decisions
The strategic thinking of the commanders determined the result of the Battle, as they moved their troops and utilized the circumstances on the battleground to gain the advantage.
Key Leadership Moments
Indeed, these moments of individual bravery and leadership were crucial because these officers on both sides motivated their troops, made them believe in themselves, and led them to victory.
Aftermath
Consequences for the Marathas
The Marathas, defeated on the battlefield, faced significant losses in both men and territory, which cut their hold over northern India and thus speeded their fall as an important political power.
British Expansion
The British East India Company won; thus, he established his authority in Delhi and extended his influence on the inner part of India; therefore, British rule was set in India.

Legacy of the Battle
Impact on Indian Politics
The Battle of Delhi redefined the political situation in India, which led to the domination of British power and the fall of the Indian rulers. Thus, the British paramountcy over the Indian princely states was the result.
Implications for British Rule
The conquest of Delhi gave the British East India Company a strategic position in northern India, which allowed them to take over important trade routes, resources, and power centers that were dominating at that time.
Historical Significance
Perspectives from Historians
Historians consider the Battle of Delhi a turning point in Indian history, which, as a result, led to the change from Mughal to British rule and the start of British colonial rule.
Lessons Learned
The Battle of Delhi shows the persistent influence of imperial rivalries, military strategy, and political activities on the path of history, therefore giving us a lot of information on the dynamics of power and conquest.
Remembering the Battle

Commemorations
Despite the time that has passed, the Battle of Delhi’s memory remains, and it is remembered by the monuments, memorials, and cultural artifacts that are important in the formation of India’s future.
Cultural References
The Battle of Delhi has been the subject of numerous literary works, paintings, and movies, thus becoming a background for novels, films, and historical accounts that aim to depict the drama and complexity of this remarkable historical event.
Conclusion
The Battle of Delhi (1803) is clear proof of the empire’s clash and the fight for supremacy in the Indian subcontinent. The memory of its legacy is still heard throughout history, showing us the vital power, politics, and desire to gain control.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What were the leading causes of the Battle of Delhi?
The Battle of Delhi was mainly a result of the expansionist policies of the British East India Company, which was aspiring to extend its control over the Indian territories, and the weakening of the Maratha Confederacy because of internal divisions and succession disputes.
Who were the critical commanders on both sides of the conflict?
The top commanders of the British were General Gerard Lake, and the Maratha Confederacy was headed by Daulat Rao Scindia and his general, Jaswant Rao Holkar.
How did the outcome of the Battle affect the Maratha Confederacy?
The loss at the Battle of Delhi caused the Maratha Confederacy to become weak, and, thus, the territory they got was reduced, and the decline of the political power of the Confederacy in India started.
What role did Delhi play in the strategic calculations of both sides?
Delhi was important in terms of strategic and historical values, as it was northern India’s leading political and commercial center and had a unique cultural significance. Being the capital, Delhi was the center of major trade routes and resources.
What were the long-term consequences of the Battle of Delhi for British rule in India?
Through the Battle of Delhi, Britain gained control over northern India and, thus, consolidated the British East India Company as the dominant power in the area, laying the ground for complete British rule in the subcontinent.
How did the Battle of Delhi shape the political landscape of northern India?
The Battle of Delhi signaled the end of the local rulers of Marathas and the rise of British power; thus, the situation in which the princely states of India in that region came under British rule was created.
Are there any famous landmarks or monuments associated with the Battle of Delhi?
Yes, there are many landmarks and monuments in Delhi, like the Red Fort and the Jama Masjid, that connect with the Battle of Delhi, and thus, they are reminders of the city’s historical importance.
What were some of the immediate aftermath effects of the Battle on Delhi’s civilian population?
The civilians of Delhi encountered the trials of being displaced and the ruination of their property, and their daily life was disturbed due to the Battle and the later British occupation.
What lessons can be learned from studying the Battle of Delhi?
Delving into what happened with the Battle of Delhi provides us with a view into the intricacies of imperial rivalries, the military tactics and strategies, and the long-lasting influence of historical events on the fate of nations and civilizations.
How is the Battle of Delhi remembered and commemorated today?
Delhi’s Battle is remembered and honored through monuments and memorials that are key to understanding the importance of its role in shaping the history and the identity of the Indians.