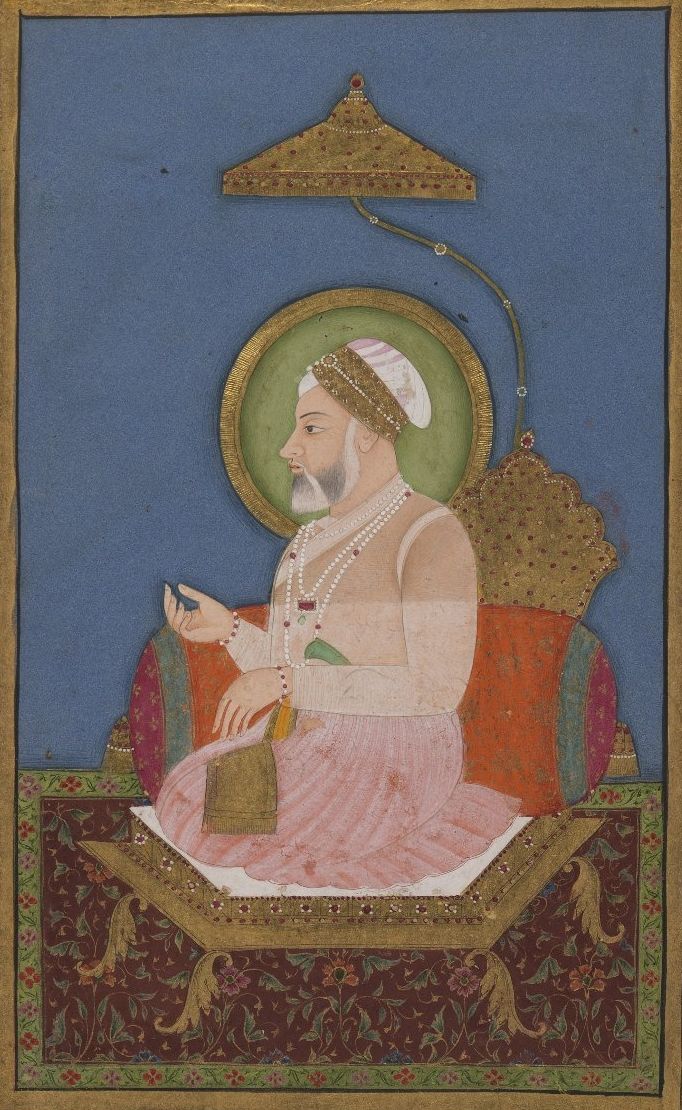
Alamgir II, also named Aziz-ud-Din, was the fifteenth Mughal emperor. He was born on 3 June 1754 and reigned from 3 June 1754 to 29 November 1759. The reign of his era not only exposed the Byzantine Empire to difficulties but offered ways for reforms to be enacted.
Early Life and Ascension of Alamgir II
Sri Mudaiah Alamgir II was born on the 6th June 1699. He was the son of Emperor Jahandar Shah. He ascended the throne, usurping the predecessor’s authority, Ahmad Shah Bahadur.
Political Environment
Emanate to an heir of a political situation with intense internecine strife, external aggressions, and overwhelming economic malaise.
Reign of Alamgir
Challenges and Reforms
It was pretty tricky for Alamgir to overcome multiple difficulties, mostly the local powers’ conflicts; among them, the Marathas and the Sikhs were examples. Moreover, he combined some internal organization and financial reforms to stabilize the Roman Empire.
Cultural and Architectural Contributions
Within the restive context of political history, Alamgir sponsored the wealth of culture by rebuilding and managing many care facilities, adding to the heritage of the Mughal Empire.
Legacy and Impact
Succession and Aftermath
Alamgir II’s rule culminated in an unfortunate way with his assassination in the so-called Battle of Battles, a historical moment that ended by augmenting the domestic political crisis, eventually damaging the Mughal authority again.
Historical Assessment
Historians are by no means unanimous on Alamgir, who is seen by some as the one who tried to eliminate the administrative problems. Still, others say he didn’t know what established the external threats.
Alamgir II: His myth and reputation in the modern culture
Literature and Artistic Depictions
Alamgir II’s life and rule are significant themes in many accounts, ranging from books and movies, which show a history full of intrigue and drama in Mughal history.
Modern Perceptions and Adaptations
In the present day, in both the writer’s and the filmmaker’s and artists’ imaginations, Alamgir is a torch bearer, illuminating an era of glory with its implications.
Conclusion
Alamgir, the fifteenth ruler of the Mughal dynasty, reigned with allotments of difficulties and cultural triumphs of his time. In doing so, he had to address numerous adversities, but he showed his authority and keen interest in art, which is still a debatable topic among historians.
FAQs about Alamgir II
- What were depictions of Alamgir, and what were his most significant successes?
- Although his reign was overshadowed by the increased taxes and difficulties in his campaigns, Alamgir established reasonable governing procedures and art patronage, which is still remembered.
- What were Alamgir’s contributions to the historical account of the Mughals?
- During the reign of Alamgir, the promises of the Mughal Empire were compromised due to several factors, such as the lack of governance and its inability to repel enemies.
- What obstacles to the rule of Alamgir II’s II’s were there?
- Alamgir had to cope with the pressure of the Marathas and the Sikhs, the domestic row, and the financial difficulties that struck his empire.
- Did Alamgir have any significant landmarks as a legacy?
- In the 12th century, Alamgir favored the construction of different buildings and monuments, but only a few remained. An object of particular importance here is the Moti Masjid in Delhi, a mosque erected by Alamgir.
- What memorialization do we have for alias Alamgir?
- Alamgir attained the status of a person from an era of Mughal history when turmoils prevailed at every turn, and the history of the empire’s decline and the sources of trouble getting beyond the kings are written in their rule.