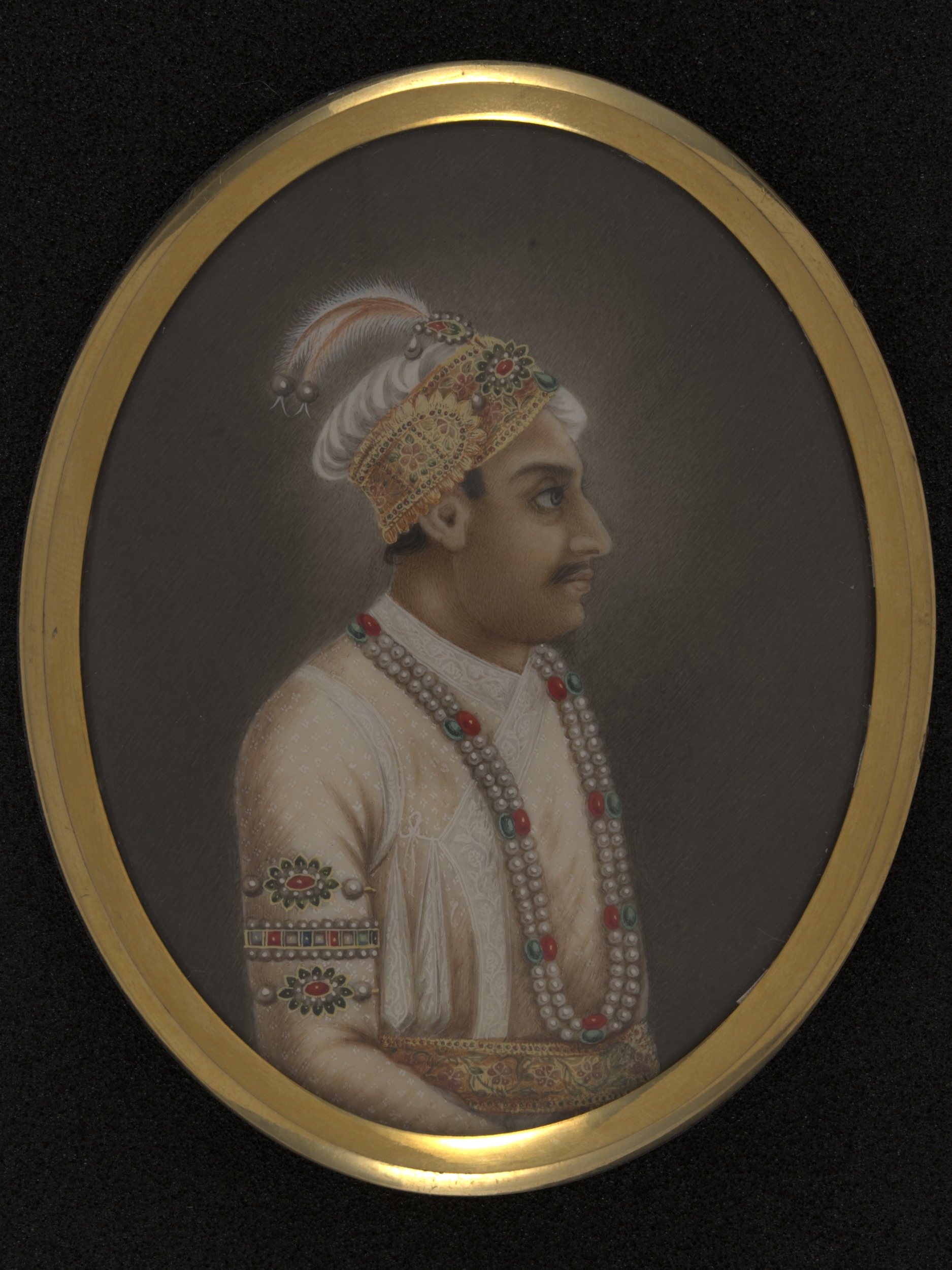
Ahmad Shah Bahadur, the fourteenth Mughal Emperor, was contemporary in Indian history and abounded with revolts. As a case study of a ruler’s biography and the disputes and contradictions in his deeds, let’s examine his life, reign and hesitations about his legacy.
Historical Context of Ahmad Shah Bahadur
From the mid-18th century till Emperor Ahmad Shah, the Mughal Empire was tumbling down and fighting for its survival, having many rivals and falling to pieces from within.
Early Life and Ascension
Accompanied by an extensive array of events, Ahmad Shah Bahadur’s path to the throne was filled with significant hardships.
Background and Family
The founding of Shahjehanabad, the new Mughal capital built under the auspices of Mughal emperor Muhammad Shah, was the fledgling world in which Ahmad Shah Bahadur was born. Likewise, he could envision the intricate problems faced in governing a vast empire by growing up there.
Ascension to the Throne
Since his father died in 1748, Ahmad Shah ascended to the Mughal throne, and predictably, the appointment became an excellent transitional task.
Reign and Challenges
During the reign of Ahmad Shah, external threats were mainly, and domestic wrecking was of life and death importance.
Marathas and Afghan Threats
All his dominion was attacked variously by great enemies such as the Marathas and Afghan invaders who dangerously pursued the erosion of Mughal dominion.
Economic Turmoil
The Muhammadan regime, representing Ahmad Shah Bahadur’s reign, experienced economic instability that worsened due to high-level corruption and erratic administration.
Personal Traits and Legacy
It cannot be overemphasized that the strong personality and military leadership of Ahmad Shah had a marked influence on the Mughal Empire.
Character and Leadership Style
The claim by some historians that Ahmad Shah was a weak and indecisive ruler was made real when he began to face direct dangers to his empire from outside forces.
Legacy and Impact
Although there were a few faults of the ruler, the legacy of Ahmad Shah was significant enough that history remembers it, continuing the transition period during which events shaped the future.
Downfall and Death
Shaha Alam defeated and plundered the Mughal territory. The demise of Ahmed Shah followed, and the region reached rock bottom.
Capture and Imprisonment
In 1754, an Afghan army led by Ahmed Shah Durrani captured Ahmad Shah, the ruler of Afghanistan at that time, and put him in prison, which was considered a significant event for the end of his reign.
Death and Aftermath
After the captivity of the Mughal Empire’s last ruler, Babar, in 1775, their direct rule of India ceased.
Assessment and Controversy
The historical diversity in the opinion about Ahmad Shah Bahadur’s reign makes it more controversial and debatable.
Historical Perspectives
Students still argue about what Ahmad Shah Bahadur’s heritage meant; those who claim them as an underdog and hold different opinions thought the ruler had weak skills.
Modern Interpretations
Nowadays, several historians are keen to put the time of Ahmad Shah into a broader historical context, fascinated by the unravelling of the Mughal Empire.
Conclusion
Under Ahmad Shah Bahadur’s rule, he carved out the complexities the Mughal Empire faced during a time riddled with decline and transition. He is remembered both in approval and disapproval among historians and experts.
FAQs
- Was Ahmad Shah? What was his personality like?
- Ahmad Shah was the 14th Mughal Emperor who presided over the entity during the middle of the 18th century; however, the stability of the state is more concern.
- A classic example would be to describe the main events during the period of his rule.
- Unlike his father, who had a raging conflict with the Marhathas and Afghan invaders, had suffered an economic setback, and in the end had been secured by Afghan soldiers, Ahmad Shah Bahadur’s reign was marked by an ongoing conflict with the Marhathas and Afghan invaders, economic turmoil, and his ultimate imprisonment by the Afghan forces.
- What could be considered the heirlooms of Atah Fattah Shir?
- The opinion about Ahmad Shah is divided; some portrayed him as a pawn in a more oversized political chessboard, while others believed that he lacked strategic and tactical leadership skills.
- What made Baji Rao decline in power?
- During the Battle of Panipat in 1754, Ahmad Shah, who was the leader of the Mughal army, was captured by the Afghan forces led by Ahmad Shah Durrani and was subsequently kept in confinement, which finally resulted in his death.
- How does the world see Mirza Ahmad Shah Bahadur Bada?
- Today’s Practitioners might take a wider angle of view of Amhad Shah Bahadur’s administration, including the progression of the Mughal Empire era and its decline. This will allow them to consider his legacy in the broader context.