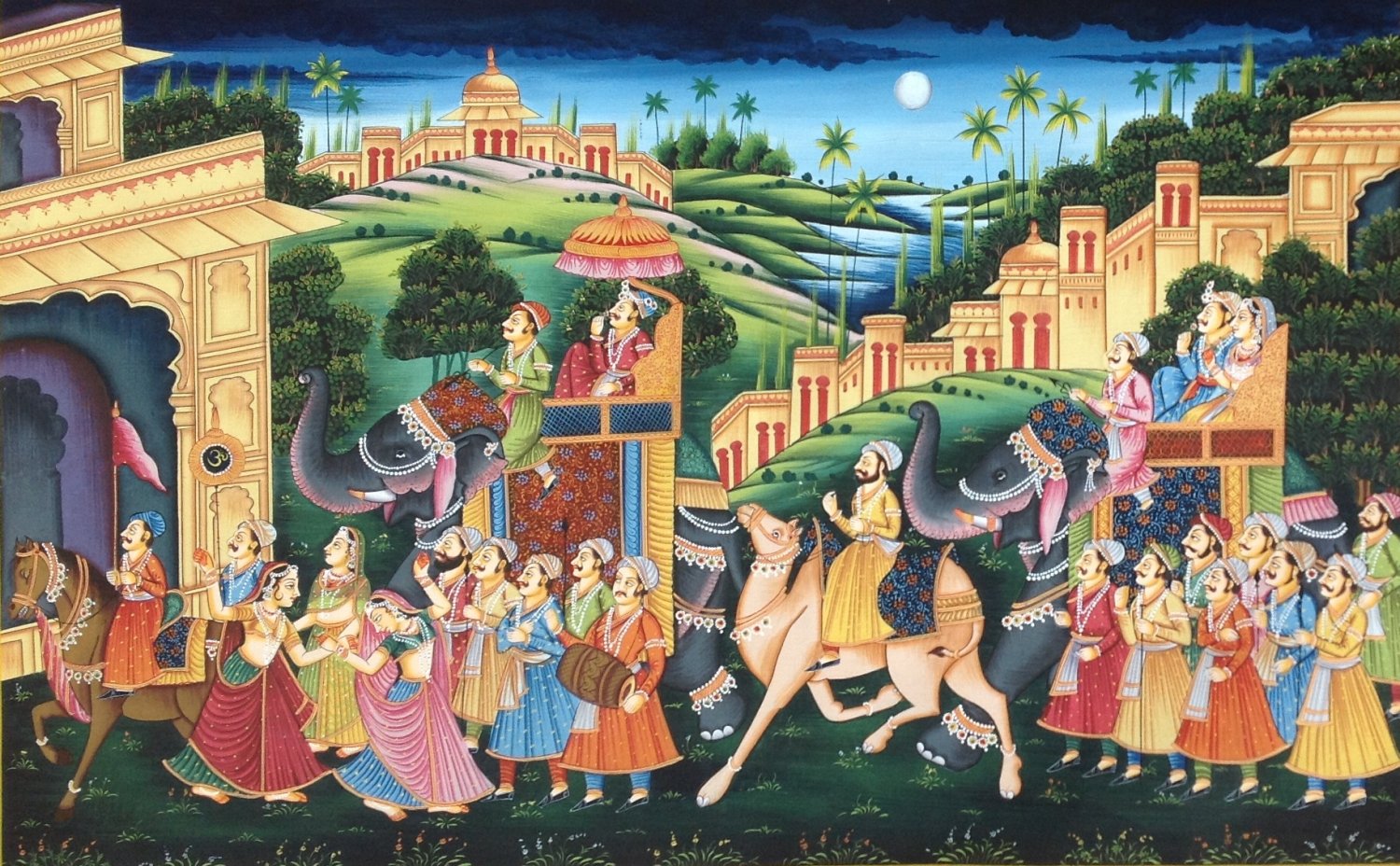
The year 1530 became a turning point in the story of The Mughal Empire; under the rule of Babur and groundbreaking trends since it built a legacy that the Mughals ruled India for over three hundred years. Here I will bring up the events of 2018 and the outcome which it caused.
Babur’s Ascension and Consolidation of Power 1530
Victory and Expansion 1530
In 1526, Babur earned a foremost position in the power struggle over the Indian subcontinent by winning the renowned battle at Panipat, which served as a base laid for the Mughal Empire. Nevertheless, this competition happened particularly in 1530 when Babur established the power and suzerainty domain of his empire.
Battle of Ghaghra 1529
One instance from the year 1530 was the Ghaghra Battle in which Babur the Mughal Emperor faced Mahmud Lodi, a well-known Afghan ruler. The issue of the Battle of Ruru near Sirohi was another victory for Babar, which led to the strengthening of his power over Northern India.

Administrative Reforms and Governance
Conquerors were forced to develop and strengthen their administrative systems to rule their new land. In 1530, first Babur introduced the bolstering of the government working through the improvement in the orderliness of it. These reforms, at the same time, paved the way for the establishment of effective regional administration and grossing of government revenues, making sure that law and order were preserved despite the diversity of the various regions under the rule of the Mughals.
Cultural Renaissance under Babur’s Patronage
Promotion of Art and Literature
While he was faced with the problem of governance and the expansion of the empire, Babur’s court was a point of cultural excellence. Poots, writers, and artists the xang integrity of the Ragana period, attracted by his praise and sponsorship moved to his court.
Poetry and Literature
Babur, not only was a great poet and writer himself, but his work, the Baburnama, is the invaluable historical record of his life in the form of an autobiography. His reminiscence, known as the “Baburnama,” as a whole, is a treasure trove wherein scholars and researchers alike can study the ruling leader’s life, conquests, and the social-cultural arena of his age. Besides that, Princess Khalbara’s reign also constituted a period of high development of Persian and Turkish literature, where there were famous poets like Mir Ali Shir Nava’i, who were patronized and acclaimed.

Architectural Marvels and Urban Development
Furthermore, Babur not only nurtured art and literature but also extended his contribution to architecture and city policies. The city of Agra is the best example of Babur’s engineering activity when he started construction projects and urban improvement programs. It will be glorified by his successors with beautiful architectural works.
Babur’s Gardens
Considering the effect of the Babur on building, the creation of beautiful gardens known as “Baghs,” goes to mention. Here, they get a place, which is well arranged and combines things like geometric disposition, greenery and water features, giving the Mughal’s aesthetic feeling a soothing retreat and symbolic place.

Legacy of 1530: Shaping the Mughal Empire’s Destiny
Foundations for Future Greatness
But the events of the 1530s, actually, literally came to pave the way for the Mughal Empire’s further prosperity. Babur’s inspired planning, his marvellous military initiatives and his support of art and culture during his rule secured the way for the empire to gain even more influence under his successors.
Transition of Power
Humayan became the heir apparent to Babur’s throne in 1530. His transition was a well-orchestrated event. The negotiations for the right to be a successor and the lull era during consolidation from this period were the tools to ensure the generations and the still-existing legacy of leadership in the Mughal dynasty.
Cultural Integration and Synthesis
One legacy of many of Babur’s reigns was his involvement in the tending of the culture of integration and synthesis. The Mughals found the solution to bridge the gaps between diverse belief systems, languages, and traditions, and so the Mughal Empire eventually became the greatest cultural melting pot in the world, where harmony and cooperation were cherished.
Religious Tolerance
An Islamic religious leader, Babur persisted with his religiously tolerant policy, which earned universal acceptance across the Mughal rulers. Behind the curtains, Babur was a Muslim ruler. He did not push his religion to the people even though he was a Muslim king. Rather he governed with justice and fairness for his subjects regardless of their religious faith.

Conclusion: Reflecting on 1530 and the Mughal Legacy
In the end, the juncture in the acme of Mughal history was the 1530 period while Babur ruled and in those years arts, literature, and architecture flourished due to his sponsorship. The events of 1530 led to the deciphering of the Mughal Empire’s success and its still-running legacy about the Indian subcontinent which is a manifestation in cultural, political and architectural aspects for centuries to come.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
- What was the outcome of the movement in the year 1530 in the Mughal Empire?
- One of the major events of 1530 is dependent on Babar’s victory over his forces, including victories at Gagara or Andhra rat and his promotion of art and culture.
- What is the legacy of Babur in the architectural style of the Mughal dynasty in 1530 A.D.?
- Babur, who is known as an influential person in the field of architecture, played a role in the development of topiaries and urban prosperity, which is where the exquisite Architecture of the late Mughal rulers originates.
- What was Babur’s art patronage role in his time and how did it induce the development of art and the literature in 1530s?
- The Mughal dynasty under Babur’s patronage of the arts and literature provided the cultural landscape of the empire with a richness that led to a diversity of the intellectual and artistic fare which thrived during the rule of subsequent kings.
- What measures did Babur take against the government system and administration of the early Mughal rule in 1530 and what the consequences were?
- Babur’s administrative reforms have therefore become a blueprint that the most effective governing practice as well as revenue-keeping methods that took place during its domination.
- What became unwrapped to future generations through His reign of 1530?
- In 1530 Babur’s success was the point which gave cultural mixture, architectural prosperity and efficiency in the government so that is why the Mughal Empire took that position for several generations.